Turkey’s New Role in Next-Gen Commercial Vehicle Transformation

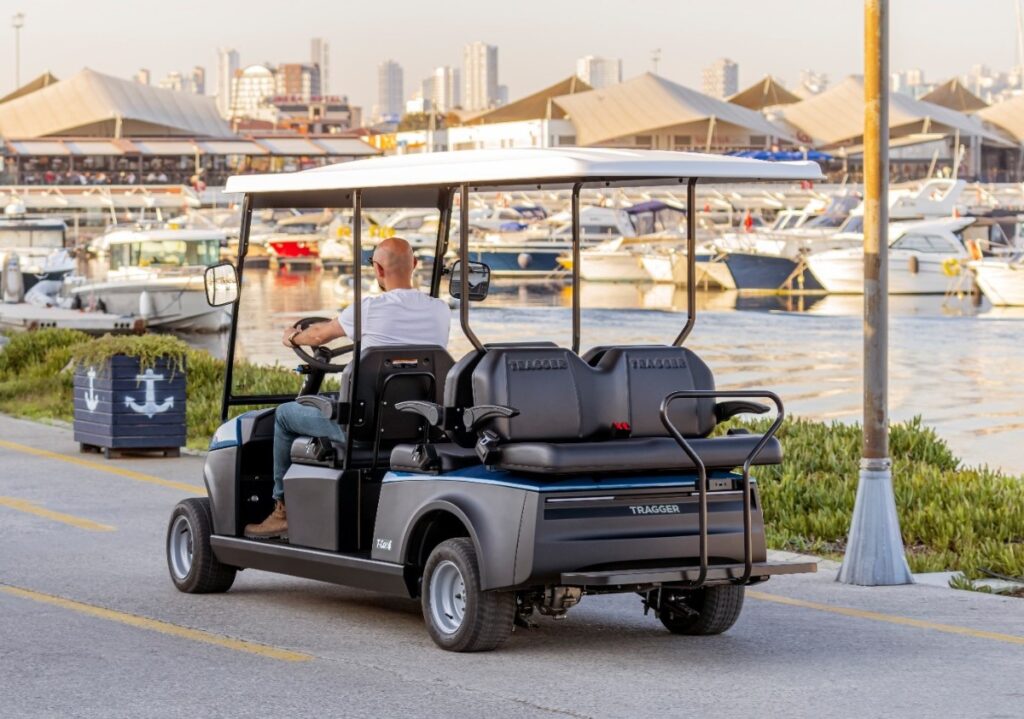
Since the late 19th century, Turkey has rapidly embraced and adopted self-propelled vehicles in parallel with Europe and the rest of the world. However, for many years, the country struggled to produce its own vehicles. It remained torn between importing and selling, producing global brands domestically, or establishing its own national brands. Despite these challenges, Turkey has a rich and diverse history in commercial vehicles. The production and use of commercial vehicles in Turkey dates back to the pre-Republic era. In the 1920s and 1930s, trucks, pickup trucks, and minibuses were used to meet transportation needs. One of the major milestones in the Turkish automotive industry came in the 1960s and 1970s, with the first domestic vehicle production initiatives. With state-supported projects, Turkey produced its first locally made car, “Anadol,” which also found commercial use. The first truck produced in Turkey, BMC Levend, entered serial production in 1966 and is considered a turning point in the country’s commercial vehicle manufacturing history. Trucks and pickup trucks quickly replaced animal-drawn vehicles, especially in long-distance freight transport. In passenger transport, buses built on truck chassis became widely used. These early examples — wooden-bodied buses mounted on truck frames — benefited from the durability and load-bearing capacity of the chassis. Starting in the early 1960s, companies like Magirus (Otokar), BMC, Mercedes-Benz (Otomarsan), KARSAN, and MAN became pioneers in bus manufacturing in Turkey, entering a race to meet the rapidly growing urban transportation needs. The 1980s and 1990s marked significant growth in both the production and use of commercial vehicles in Turkey. Truck and pickup production increased notably, and commercial vehicles produced by both local and international companies began to dominate the logistics sector. From the early 2000s onward, the Turkish automotive industry continued to grow rapidly. With increasing investments from global automotive giants and the establishment of production facilities in Turkey, both the variety and quality of commercial vehicles significantly improved. Today, Turkey takes pride in being the commercial vehicle hub of Europe, successfully developing and producing both domestic and international brands at the highest quality and exporting them worldwide. As we enter the new era of mobility, commercial vehicles — already a global and national success story—are poised to write another chapter. In this new phase, the sector has a crucial mission to contribute to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future.

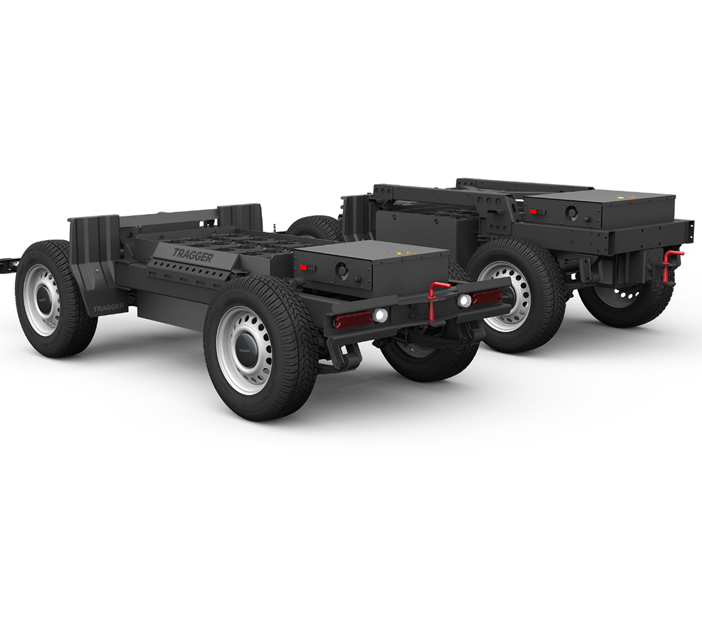
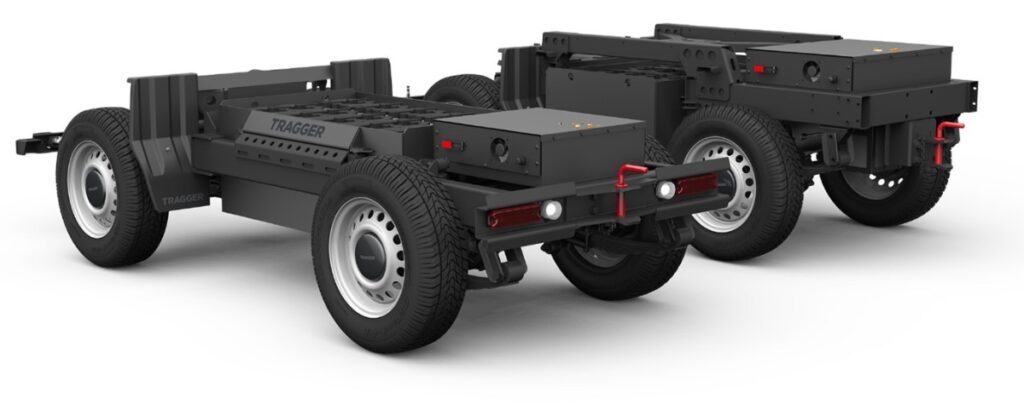
New-generation commercial vehicles are undergoing a significant transformation as a result of technological advancements and sustainability-driven developments. With electric drive systems, they operate more efficiently and reduce energy consumption; with autonomous driving technologies, they enhance ease of use; by minimizing accidents and malfunctions, they increase productivity; through constant connectivity, they optimize routes and enable more effective time use; and by supporting shared usage, they help optimize existing resources. Electrification: New-generation commercial vehicles are moving toward electric and hybrid technologies. Compared to fossil fuels, electric commercial vehicles produce significantly lower emissions and offer an environmentally friendly transportation solution. This plays an important role in improving air quality and reducing carbon footprint. Automation: These vehicles are equipped with autonomous driving technologies, enabling them to travel without driver intervention. Autonomous commercial vehicles aim to deliver safer and more efficient transportation, while reducing driver fatigue and increasing workforce productivity. Connectivity and data analytics: New-generation commercial vehicles are equipped with internet connectivity and smart technologies. Their ability to communicate with each other and with their surroundings improves safety, efficiency, and maintenance processes. In addition, the analysis of data collected from these vehicles helps optimize transportation operations. Flexibility and versatility: New-generation commercial vehicles offer flexible configuration options. Modular designs and adaptability allow them to be tailored to various business needs, enabling their use across many different industries and applications. Electric commercial vehicles can become significantly more streamlined compared to their predecessors. Platforms consisting of just one motor, its control unit, and four wheels can be transformed into various models with different body structures. This allows for simplified product development, manufacturing, and supply chains—making fast product delivery and responsive solutions possible. Electric vehicle technology involves fewer moving parts and a less complex structure compared to internal combustion engines. This simplifies production and assembly processes and enables a more minimalistic vehicle design. Moreover, key components like batteries and electric motors can be placed more compactly, saving interior space. This results in increased usable volume and load capacity. Electric vehicles also offer higher energy conversion efficiency compared to internal combustion engines, enabling lower energy consumption and longer range. For transportation businesses, this means lower operating costs and a more sustainable business model. Leaner and more efficient commercial vehicles not only reduce fuel consumption but also minimize environmental impact.
Saffet Çakmak
Sürdürülebilirlik GönüllüsüMore
Sustainable Development Goals
From Super-Intelligent Engineers to the Era of AI-Powered Assistants…
From Super-Intelligent Engineers to the Era of AI-PoweredAssistants…Another story of digital transformation Artificial intelligence (AI),…
Turkey’s New Role in Next-Gen Commercial Vehicle Transformation
Turkey’s New Role in Next-Gen Commercial Vehicle Transformation Since the late 19th century, Turkey has…
Contact
Quick Access